|
|
|
 |
|
|
| |
 Middleware Middleware
|
|
RFID/USN middleware UNIBA collects and clean mass data, summarizes it into information, and conveys it to the applicable application system, supporting stable service and minimized system backup even when multiple units are installed according to the future sophistication business, and solving the problem of compatibility with other systems. On the basis of major elemental technologies, such as automatic recognition technology, data collection, and networking technology, this product can make it easier for process management and provide a comfortable development environment. |
| |
|
|
Data Management
|
Creating meaningful data through tag data cleaning, redundant data elimination, data collection and classification (through the application of the data filtering, summarizing, and inquiring algorithm and DB technology)
Data management for tag IDs, coordinators, receiver IDs, and location information.
|
|
Process & Device Management
|
The system structure that can flexibly respond to a variety of processes (expandabiliy and flexibility)
Provide the standardized interface for the management and operation of a variety of readers, receivers, and heterogeneous devices.
|
|
Flexible Application
|
Can support various applications that operate with UNIBA
Real-time integration of various applications operating with UNIBA.
Provide the flexible interoperability with various legacy systems.
|
|
Messaging Technology/Component-Based
|
To ensure the interoperability of the existing automatic identification system in varying e-tag environments, the component-based design is used, which complies with the standardized codes and the Information and Content Exchange Protocol, meets a variety of features, depending upon the application areas of messaing technology to exchange automatic identification data, and facilitates the development and addition of new algorithms and features suitable for application services.
|
|
| |
 |
| |
 Middleware Overview Middleware Overview
|
|
|
| |
 Key Features of Middleware Key Features of Middleware
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Data Management
|
Vast amounts of tag data make it impossible for the direct use in the related application
Create meaning data through tag data cleaning, redundant data elimination, and data collection
Data management for tag IDs, reader IDs, and reader location information
|
|
| Process Management
|
The system structure that can flexibly respond to a variety of processes
Can flexibly respond to the change and expansion on the site.
|
|
| Device Managment
|
| Provide the standardized interface for the management and operation of a variety of readers, receivers, and heterogeneous devices.
|
|
| Flexible operation of applications
|
Provide various Application with UNIBA.
Real-time integration of various applications operating with UNIBA.
Provide the flexible interoperability with various legacy systems.
|
|
| Easy and user-friendly interface
|
| The system structure that can be easily used in any environment.
|
|
|
|
|
 Features of Middleware Features of Middleware
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Application of Messaging Technology
|
| To ensure the interoperability of the existing automatic identification system in varying electronic tag environments, messaging technology is used to comply with the standardized codes and the Information and Content Exchange Protocol, and to exchange automatic identification information.
|
|
|
DB Technology
|
| Apply the algorithm and DB technology capable of efficient filtering, summary, and inquiry of data stream arising in real time from a number of tags and sensors
|
|
|
Component-Based
|
| The component-based design is used to meet a variety of features, depending upon the application area, and to facilitate the development and addition of new algorithms and features suitable for application services.
|
|
|
Automatic Control
|
| Enables automatic identification that automatically runs and controls the related system through the real-time detection of events occurring in the electronic tags environment.
|
|
|
| |
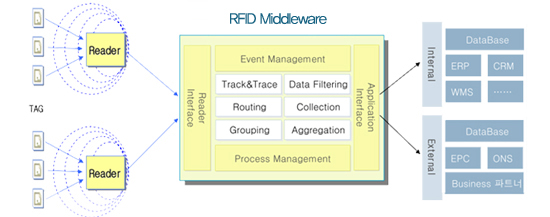
 Middleware Architecture Middleware Architecture
|
|
| |
 Expectations of Middleware Expectations of Middleware
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cost Reduction
|
An analysis of the RFID/USN system has found that reducing costs or increasing value added that companies need does not arise from such hardware as an RFID tag or a reader.
UNIBA, loaded with all the new features of storing, managing, and analyzing vast amounts of data, plays a key role in reducing costs and increasing value added. |
|
|
Efficient Data Management
|
UNIBA performs the function as the integration of hardware and as data filtering.
UNIBA is in charge of communications between the company¡¯s legacy system and RFID system, re-configuring a vast amount of raw data into actually meaningful information and data, thus reducing the amount of data.
|
|
|
System Configuration
|
Symplicity: Can be easily connected to any kind of device, any application, regardless of knowledge of the complicated specifications or of the interfacing of individual devices.
Durability: UNIBA stores data for a certain period of time and can provide this to outside applications if necessary.
Standard: The uniform, standardized access is given to all devices and applications.
Expandability: Allows easy processing without causing damage to the entire system in case of system additions/modifications and for business process additions/changes. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|


